Subtalar Varus - Over Pronation
One of the most common causes of foot and leg discomfort is a condition known as subtalar varus or over pronation. Normal pronation or "turning inward" of the foot is necessary as the foot adapts to the ground. With excessive pronation/ over pronation, the arch flattens, collapses, and soft tissues stretch. This causes the joint surfaces to function at unnatural angles to each other. When this happens, joints that should be stable now become very loose and flexible.
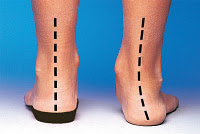
At first, excess pronation may cause fatigue. As the problem gets worse, strain on the muscles, tendons, and ligaments of the foot and lower leg can cause permanent problems and deformities.
Symptoms:
When standing, your heels lean inward and one or both of your knee caps turn inward. Conditions such as a flat feet or bunions may occur and you develop knee pain when you are active or involved in athletics. The knee pain slowly goes away when you rest. You abnormally wear out the soles and heels of your shoes very quickly.
Symptoms can manifest in many different ways. The associated conditions depend on the individual lifestyle of each patient. Here is a list of some of the conditions associated with Subtalar Varus or Excess Pronation:
- Hallux Abducto Valgus - Bunions
- Hallux Rigidus - Stiff 1st toe
- Heel Pain - Plantar fasciitis
- Arch pain
- Metatarsalgia - Forefoot pain
- Ankle sprains
- Shin Splints
- Achilles Tendonitis
- Osteochondrosis
- Knee Pain
- Corns and Calluses
- Hammer Toes
- Flat Feet
Over pronation occurs due to a biomechanical dysfunction (walking abnormality). It can be congenital or environmental; Rigidity of terrain, hard soled shoes, excessive weight and lack of muscle toning. This can often be controlled via insoles, weight loss, exercise and/or orthotics.